Business Visualizations
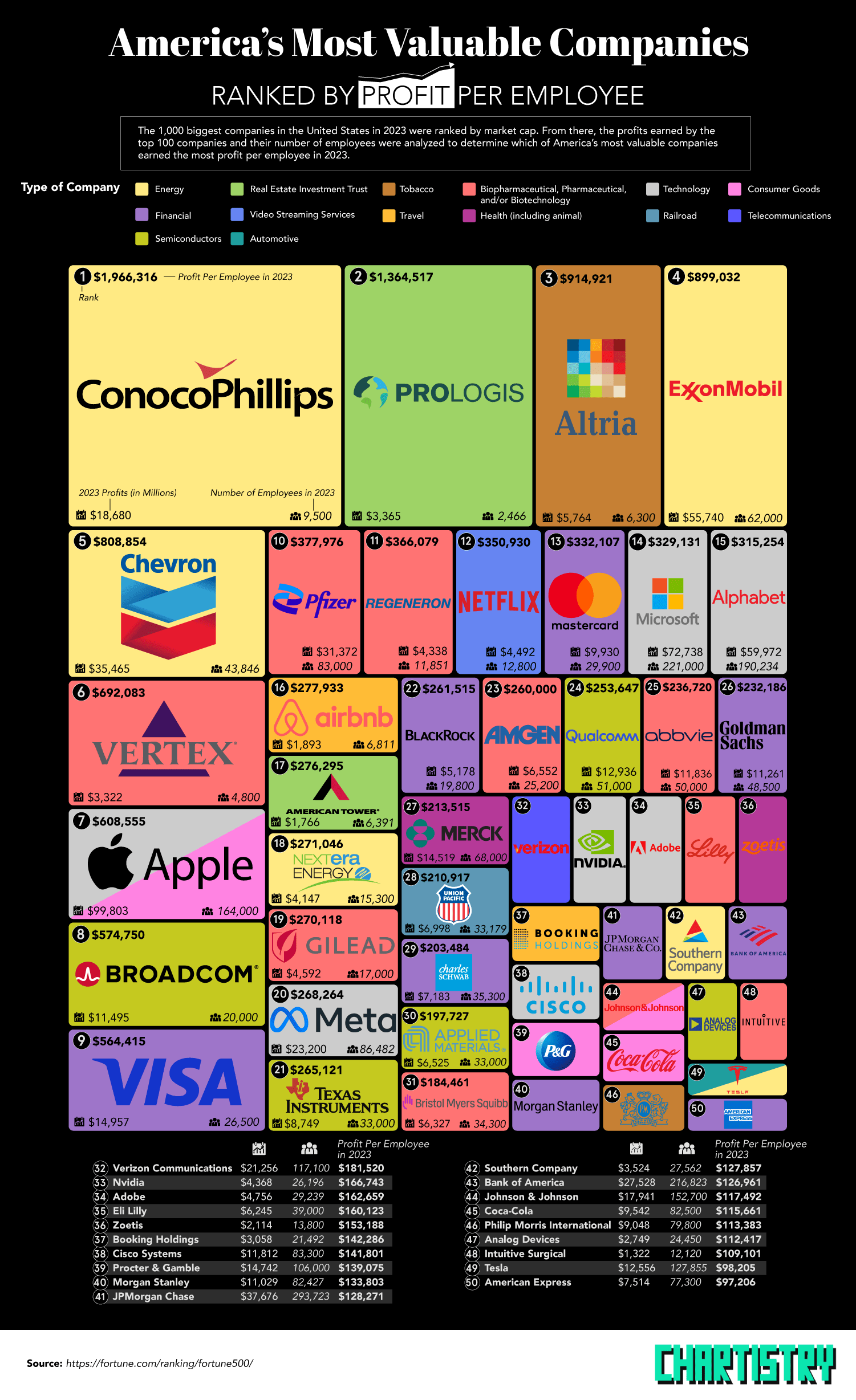
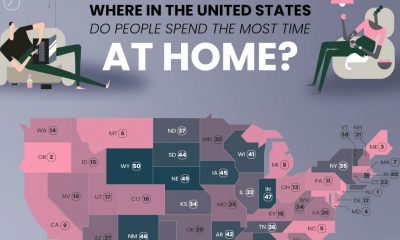
America’s Most Valuable Companies Ranked by Profit per Employee
Ever wonder how much money major corporations make per employee? Profit Per Employee (PPE) is determined by dividing the company’s profit by the company’s quantity of full-time employees. The most profitable companies may not necessarily be the most profitable by number of employees—and vice versa. Whenever the economy is uncertain, this formula is usually one of the metrics companies will monitor to determine the efficiency and productivity of their staff. Using data over profit and company size from 2023, our team at The Chartistry has ranked the top 50 companies with the highest profit per worker.
Click below to zoom
With a profit of nearly $2 million for each of their 9,500 employees, ConocoPhillips ranks first for highest profit per employee by quite the large margin. ConocoPhillips, an American oil and gas producer, saw a total profit almost $18.7 billion in 2023. Since oil and gas are two of the most valuable energy commodities in the world, it is not uncommon for an energy company to rank high in terms of PPE since their net profit is typically quite expansive. Of the top 50 companies with the highest profit for every employee, six of them can be categorized under the energy sector.
Coming in second place, Prologis is an investment trust company that saw a total profit of $3.4 billion in 2023. This profit was divided by their 2,466 employees to end with a profit of $1.36 million per employee.
In third, there is the tobacco company Altria Group. Altria Group’s 2023 profit of $5.8 billion was divided by 6,300 employees to result in a profit per employee of $915 thousand. Tobacco is yet another commodity product, with only one other tobacco company making the top 50 ranking.
Exxon Mobil is another oil and gas company with high profit per employee, coming in fourth place. Out of their profit of $55.7 million in 2023, their 62,000 employees averaged a profit of $899 thousand each.
Rounding out the top 5 companies is Chevron, the third oil and gas energy company in the top companies by profit per employee. With a total profit of $35.3 million, their PPE comes out to $809 thousand for each of their 43,846 employees.
Some companies land rank in both the most profitable in the world overall as well as in profit per worker. Apple, for example, brought in a 2023 profit of nearly a $100 billion. The company itself is valued at a total of $2.1 trillion. They managed a PPE of $609 thousand for their 164,000 employees, making them seventh among all companies.
Why is Profit per Employee Important?
For every company with an impressive profit per employee, there are tens, hundreds, even thousands of people working at the front line and behind the scenes to keep operations running as smoothly and efficiently as possible. PPE, not to be confused with Revenue per Employee, is a way for the company to measure the performance and productivity of the average employee in any given workforce to judge their added value. In other words, a way to know if their investment in hiring, retaining, and training their employees returned desirable results. Of course, it isn’t and shouldn’t be the only method to judge the value of an employee. When used in combination with other metrics, however, it can be a helpful tool to see the what employees have brought to the company.
For the majority of situations, a healthy profit per employee will be a good indicator of the health of the company at large. It shows that the business is properly maximizing the streamlining of their operations and utilizing the talent of each employee. This performance can mean that an underwhelming PPE may lead to cost-cutting measures for the company. Oftentimes, this is in the form of employee layoffs in areas that may not be contributing to the overall profit.
Did You Enjoy this Original Visualization by The Chartistry?
If you enjoyed this visualization and analysis by The Chartistry, check out the other original visualizations we’ve created. For even more great content, check out our collection of curated business and finance visualizations. If you love this visual content so much that you want your own, let us know; We design custom visual content for customers too!
The Profit per Employee of the Largest Companies in the U.S. By Market Cap (The Full List)
Which corporations have the highest revenue per employee? Companies that are able to do more with less:
| Rank | Name | Type of Company | 2023 Profits (in Millions) | Number of Employees in 2023 | Profit per Employee in 2023 |
| 1 | ConocoPhillips | Energy | $18,680 | 9,500 | $1,966,316 |
| 2 | Prologis | Real Estate Investment Trust | $3,364.9 | 2,466 | $1,364,517 |
| 3 | Altria Group | Tobacco | $5,764 | 6,300 | $914,921 |
| 4 | Exxon Mobil | Energy | $55,740 | 62,000 | $899,032 |
| 5 | Chevron | Energy | $35,465 | 43,846 | $808,854 |
| 6 | Vertex Pharmaceuticals | Biopharmaceutical, Pharmaceutical, and/or Biotechnology | $3,322 | 4,800 | $692,083 |
| 7 | Apple | Technology, Consumer Goods | $99,803 | 164,000 | $608,555 |
| 8 | Broadcom | Semiconductor | $11,495 | 20,000 | $574,750 |
| 9 | Visa | Financial | $14,957 | 26,500 | $564,415 |
| 10 | Pfizer | Biopharmaceutical, Pharmaceutical, and/or Biotechnology | $31,372 | 83,000 | $377,976 |
| 11 | Regeneron | Biopharmaceutical, Pharmaceutical, and/or Biotechnology | $4,338.4 | 11,851 | $366,079 |
| 12 | Netflix | Video Streaming Services | $4,491.9 | 12,800 | $350,930 |
| 13 | Mastercard | Financial | $9,930 | 29,900 | $332,107 |
| 14 | Microsoft | Technology | $72,738 | 221,000 | $329,131 |
| 15 | Alphabet | Technology | $59,972 | 190,234 | $315,254 |
| 16 | Airbnb | Travel | $1,893 | 6,811 | $277,933 |
| 17 | American Tower | Real Estate Investment Trust | $1,765.8 | 6,391 | $276,295 |
| 18 | NextEra Energy | Energy | $4,147 | 15,300 | $271,046 |
| 19 | Gilead Sciences | Biopharmaceutical, Pharmaceutical, and/or Biotechnology | $4,592 | 17,000 | $270,118 |
| 20 | Meta Platforms | Technology | $23,200 | 86,482 | $268,264 |
| 21 | Texas Instruments | Semiconductor | $8,749 | 33,000 | $265,121 |
| 22 | BlackRock | Financial | $5,178 | 19,800 | $261,515 |
| 23 | Amgen | Biopharmaceutical, Pharmaceutical, and/or Biotechnology | $6,552 | 25,200 | $260,000 |
| 24 | Qualcomm | Semiconductor | $12,936 | 51,000 | $253,647 |
| 25 | AbbVie | Biopharmaceutical, Pharmaceutical, and/or Biotechnology | $11,836 | 50,000 | $236,720 |
| 26 | Goldman Sachs Group | Financial | $11,261 | 48,500 | $232,186 |
| 27 | Merck | Health (Including Animals) | $14,519 | 68,000 | $213,515 |
| 28 | Union Pacific | Railroad | $6,998 | 33,179 | $210,917 |
| 29 | Charles Schwab | Financial | $7,183 | 35,300 | $203,484 |
| 30 | Applied Materials | Semiconductor | $6,525 | 33,000 | $197,727 |
| 31 | Bristol-Myers Squibb | Biopharmaceutical, Pharmaceutical, and/or Biotechnology | $6,327 | 34,300 | $184,461 |
| 32 | Verizon Communications | Telecommunications | $21,256 | 117,100 | $181,520 |
| 33 | Nvidia | Technology | $4,368 | 26,196 | $166,743 |
| 34 | Adobe | Technology | $4,756 | 29,239 | $162,659 |
| 35 | Eli Lilly | Biopharmaceutical, Pharmaceutical, and/or Biotechnology | $6,244.8 | 39,000 | $160,123 |
| 36 | Zoetis | Health (Including Animals) | $2,114 | 13,800 | $153,188 |
| 37 | Booking Holdings | Travel | $3,058 | 21,492 | $142,286 |
| 38 | Cisco Systems | Technology | $11,812 | 83,300 | $141,801 |
| 39 | Procter & Gamble | Consumer goods | $14,742 | 106,000 | $139,075 |
| 40 | Morgan Stanley | Financial | $11,029 | 82,427 | $133,803 |
| 41 | JPMorgan Chase | Financial | $37,676 | 293,723 | $128,271 |
| 42 | Southern Company | Energy | $3,524 | 27,562 | $127,857 |
| 43 | Bank of America | Financial | $27,528 | 216,823 | $126,961 |
| 44 | Johnson & Johnson | Biopharmaceutical, Pharmaceutical, and/or Biotechnology | $17,941 | 152,700 | $117,492 |
| 45 | Coca-Cola | Consumer Goods | $9,542 | 82,500 | $115,661 |
| 46 | Philip Morris International | Tobacco | $9,048 | 79,800 | $113,383 |
| 47 | Analog Devices | Semiconductor | $2,748.6 | 24,450 | $112,417 |
| 48 | Intuitive Surgical | Biopharmaceutical, Pharmaceutical, and/or Biotechnology | $1,322.3 | 12,120 | $109,101 |
| 49 | Tesla | Automotive, Energy | $12,556 | 127,855 | $98,205 |
| 50 | American Express | Financial | $7,514 | 77,300 | $97,206 |
Business Visualizations
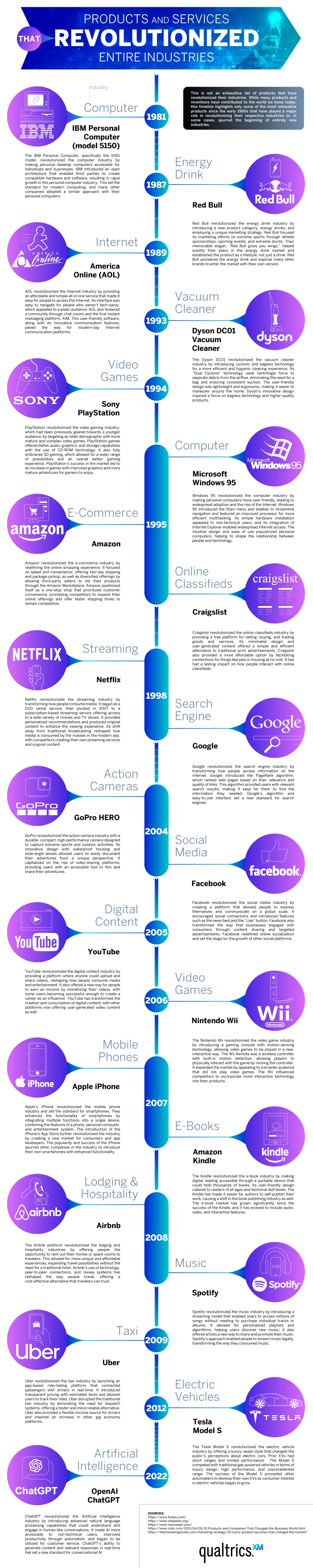
Exploring Technology That Revolutionized Industries
Breakthroughs in technology can revolutionize industries and even give birth to new industries previously unimagined. The Qualtrics team explored the world’s most revolutionary products and services, arranged on a timeline that teaches us not only which tech has caused the biggest changes, but also how these developments interact with each other and advance technology and our lives as a whole. The timeline spans 1981 to 2022. It covers the realms of Computing and Internet, Entertainment and Media, and Mobile and Digital Services. Each item on the timeline has changed its industry and even changed the way humans live.
In the world of computing and Internet services, the timeline covers:
- IBM Personal Computer
- America Online
- Microsoft Windows 95
- Google Search Engine
- OpenAI ChatGPT
Click below to zoom.
The timeline covers the world of entertainment, featuring Sony PlayStation, Amazon, Craigslist, Netflix, Facebook, YouTube, and Nintendo Wii as the gamechangers. In the mobile and digital services realm, there’s a surprising diversity of products from smartphone models to apps like Uber to the Dyson DC01 Vacuum Cleaner, and even Red Bull energy.
It’s no secret that the personal computer revolutionized the business and computing industries. Before IBM’s PC, there was no market for personal computers; today, they’re a staple of modern life. Another 1980s brand, Red Bull, created a market where none previously existed. People traditionally get their caffeine fix from coffee, but energy drinks offer an easier-to-grab option on the go. Red Bull partnered with extreme-sports marketing to turn energy drinks into a lifestyle.
The timeline highlights AOL Instant Messenger as the Internet’s first big revolution. It’s a precursor to social media and helped make the World Wide Web a means of quick, easy communication. In 1998, Google Search Engines made the Internet an invaluable tool for knowledge. Google made it far easier to find websites of value on any topic under the sun (and even some beyond!)
From here on, the timeline is dominated by a range of innovative apps and Internet-based services. Amazon is the worldwide leader in e-commerce. It changed the way consumers shop forever, offering low prices, convenience, and fast delivery. Netflix changed the way people consume films and television by offering the first-ever streaming service. They offer an enormous library of new and old titles. No more waiting for a syndicated show to air. Netflix created a demand for “binge-worthy” content. The entertainment world touches every area of traditional arts and media. We see the Amazon Kindle changing how many book lovers read, offering a digital library that saves physical space and even money for some titles. Spotify became the leader of music streaming in 2008. Some think of it as the Netflix of music. Memberships offer unlimited streaming access to millions of songs and artists.
These are just a few of the industries that have been revolutionized by technology. We haven’t even touched on AI! Dive into the timeline to learn more about the most pivotal products and services of the modern era.
Business Visualizations
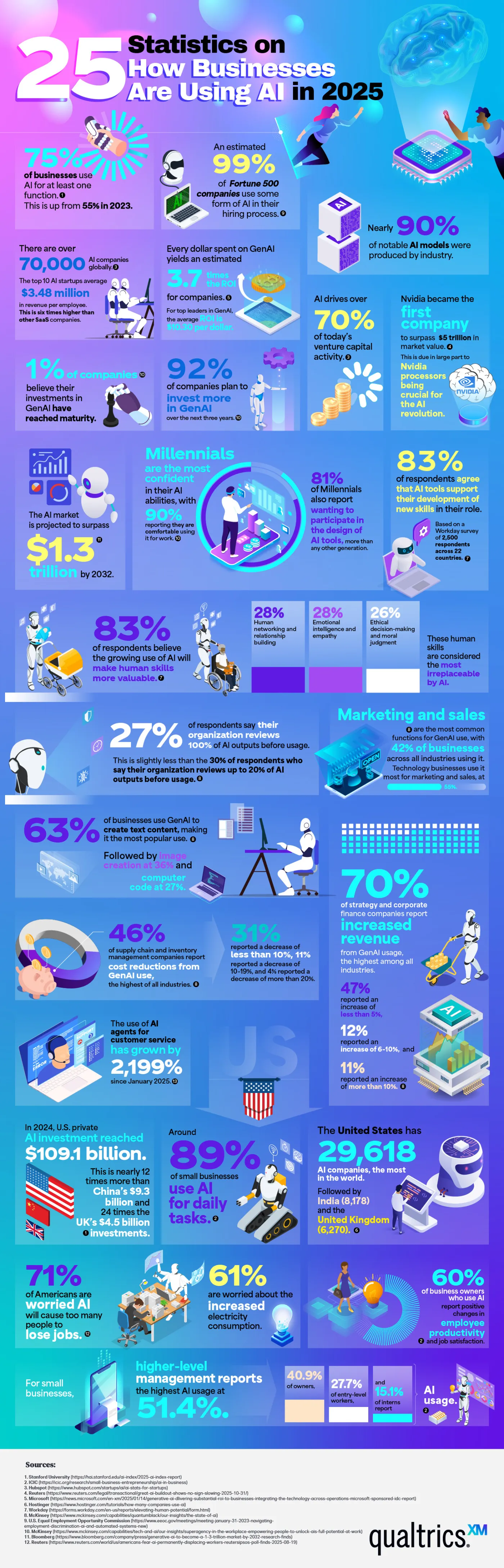
Statistics Are the Key to Understanding AI’s Influence on Business
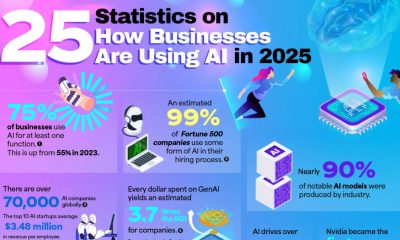
“Artificial intelligence” may be the biggest buzzword of 2026. It seems like every industry is incorporating AI into its practices, but it has had the biggest impact in the business sector. Nearly 80% of businesses use AI in some way. Qualtrics has quantified the massive impact AI has on business with a chart listing 25 key statistics that illustrate its influence. These statistics help us understand how and why businesses are using AI to reach the next level.
Many of the statistics listed show why businesses are so drawn to AI. In 2025, three out of four companies used AI regularly for at least one task. 99% of Fortune 500 companies use AI in their hiring process to screen applicants for predicted success in a role. 83% of business professionals say they’re using AI to learn new skills to further their career. Perhaps the most compelling reason businesses turn to AI is their profits. Every dollar invested in generative AI yields an average return of $3.70. Businesses are embracing what they see as AI’s stronger performance and competitive edge.
There is no doubt that AI is profitable, as these figures show. 70% of companies report increased revenue that they attribute to generative AI. Supply chains use AI to streamline logistics, and on the marketing side of business, 42% report using AI for content generation. Customer service has seen a huge explosion in AI usage, almost a 2000% increase.
AI has strong momentum, with about 70,000 companies using it globally. U.S. private investment in AI is around $109.1 billion. 90% of the world’s AI models are the work of private industry rather than government-funded research or academia, highlighting that business not only uses AI but also fuels its creation.
Small businesses are a part of these statistics. 89% of small businesses use AI in their daily operations, often for financial management and customer service. 60% of small business owners say AI has improved their employees’ productivity. Executives and senior managers are the most avid users of AI, but use by interns and entry-level employees rises every year.
Here are a few other jaw-dropping statistics that show how enormous a presence AI has in the business industry:
- AI drives over 70% of venture capital activity.
- 92% of companies plan to invest more in AI within the next three years.
- 63% of businesses use AI to generate text-based content.
- The use of AI customer service agents has grown by 2,199% since January.
- The United States is home to 29,618 AI companies, which is more than any other country.
These statistics underscore that AI is becoming a regular part of everyday business practices. Companies often say they believe AI amplifies their employee’s natural talents. Whether used for strategy, customer service, or content generation, it seems AI is here to stay.
Business Visualizations
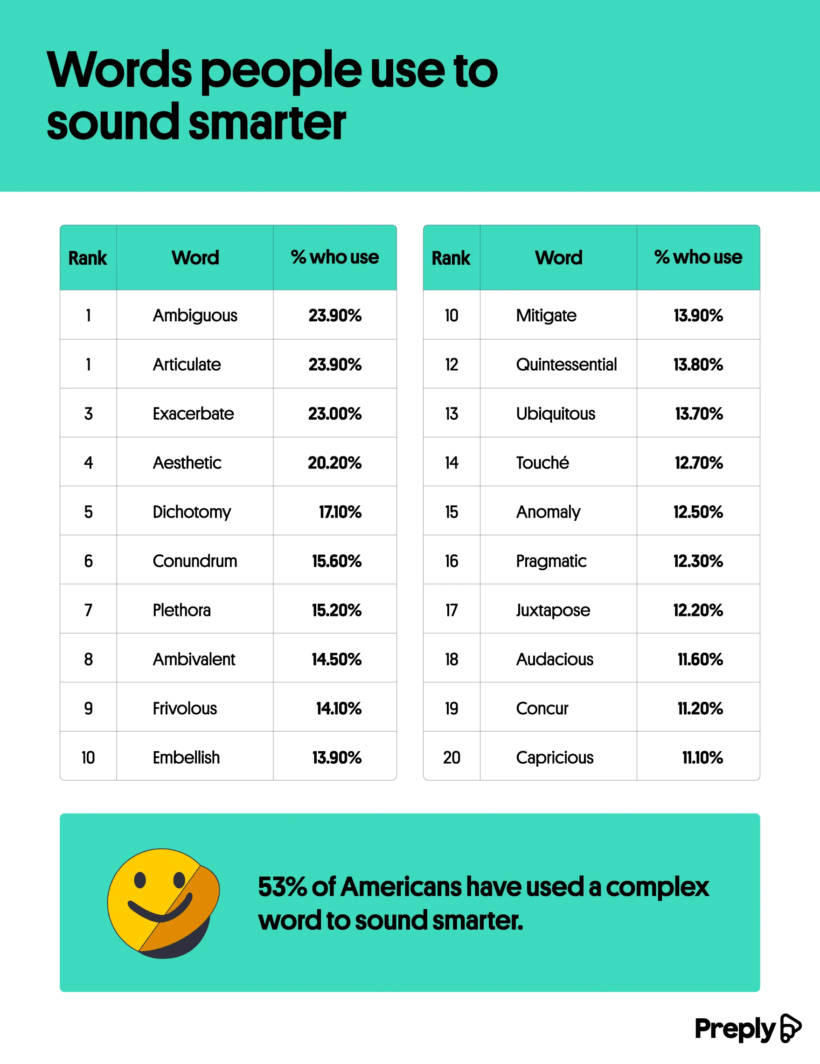
Discover the Words That Make You Sound Smarter
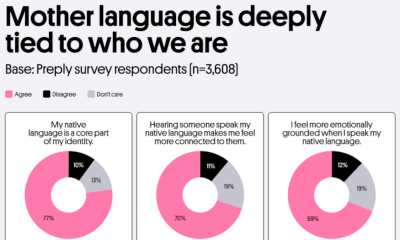
Vocabulary can reflect aspects of our personality, and it certainly affects first impressions. Many people would prefer to sound intelligent, so the team at Preply examined which words Americans think make other people sound smarter. Regardless of findings, remember that context matters the most when it comes to vocabulary! People react well to skilled communicators and sometimes big words needlessly complicate your message. But if you want to learn some new words and spice up your vocabulary, look no further than Preply’s fun and fascinating findings.
Click below to zoom.
The team asked Americans which words they use to sound smarter and these were the top ten results:
- Ambiguous
- Articulate
- Exacerbate
- Aesthetic
- Dichotomy
- Conundrum
- Plethora
- Ambivalent
- Frivolous
- Embellish
- Mitigate
As for who uses “big words” and how often, results varied. Half of Americans reported using complex vocabulary multiple times a week. A little over half of Americans admitted that they’ve purposely used complex words to create an impression of intelligence. Gen Z was the most likely to report using vocabulary to appear smarter. 24% even admitted to using a big word, even though they didn’t know the meaning.
People report using impressive words at work, school, and home. Many Americans say they’re impressed by people who use big words at work. 58% of people have used them in job interviews or while networking to give the impression of knowledge and skill. Only 17% of the team’s survey respondents said they automatically assume complex words indicate that someone has more money and success.
35% of survey takers used complex words as a tool of intimidation and said they use them during fights and arguments. Apparently, big words mean power to some people. As for vocabulary choices on a date, the picture shifts. 34% of respondents said they use complex words on a date, but that might be a misstep. 35% of people feel their dates are pretentious when they use lofty language. 27% of daters say they are attracted to people with an impressive vocabulary, so, like all things in dating, you have to find the right person. Gen Xers are the most likely to be impressed by their date’s vocabulary. Big words are no deal breakers. Only 16% of people say that overusing complicated words would ruin the date.
There’s such a thing as taking your vocabulary too far. Half of Americans say they’re annoyed by people who use complex words in everyday conversation. 29% of people said they have tried to end a conversation with someone using unnecessarily complicated words. These were words survey takers thought made the speaker sound pretentious:
- Capricious
- Equanimity
- Sycophant
- Ephemeral
- Ubiquitous
- Dichotomy
- Juxtapose
- Quintessential
- Fastidious
- Incongruous
Notice that some of these words also appeared on the list of words that make others sound smart, so bear in mind that what impresses one person can irritate another. Learning new words is a positive pursuit that can inspire and broaden your horizons, but remember to consider the right time and place for more unusual words.
-

 Business Visualizations1 year ago
Business Visualizations1 year agoEverything Owned by Apple
-
 Business Visualizations1 year ago
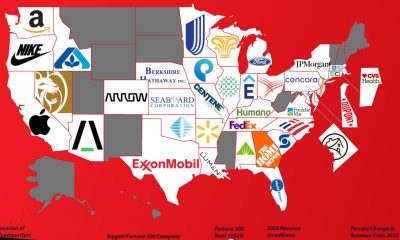
Business Visualizations1 year agoThe Biggest Fortune 500 Company in Every State
-

 Business Visualizations10 months ago
Business Visualizations10 months agoThe Biggest Employers by Industry
-
 Business Visualizations2 years ago
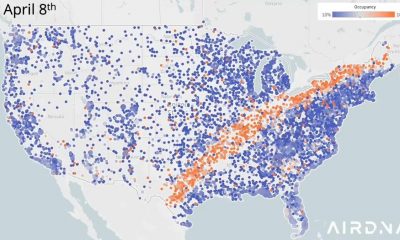
Business Visualizations2 years agoNew Animated Map Shows Airbnb’s Fully Booked Cities Along the 2024 Eclipse Path of Totality
-

 Business Visualizations2 years ago
Business Visualizations2 years agoEverything the Luxury Giant LVMH Owns in One Chart
-
 Timelines1 year ago
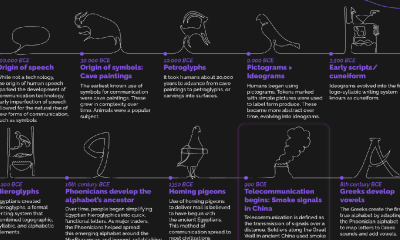
Timelines1 year agoTimeline Charts the Development of Communications Technology
-

 Charts2 years ago
Charts2 years agoHow Many Crayola Crayon Colors Are There? A Lot.
-

 Business Visualizations5 months ago
Business Visualizations5 months agoThe Largest Companies in America That Are Still Run by the Person Who Founded Them