Business Visualizations
Everything Owned by Apple
Apple Inc. has long been renowned for its innovation and cutting-edge contributions to technology. In the fifty years since its founding, Apple has gone from an obscure niche brand to one of the most well-known companies in the world. Throughout its history, Apple has acquired over 100 companies, some of which became core aspects of Apple’s brand. Since its inception, Apple has become nothing short of a cultural and economic phenomenon. This chart, which was created by the team at The Chartistry, takes a look at who founded Apple, the companies Apple owns, the many products they’ve created and sold throughout the years, and Apple’s largest stock holders.
Click below to zoom
A Brief History of Apple
Before it was the tech giant we know today, Apple had surprisingly humble roots. Apple Inc. was founded on April 1, 1976, by Steve Jobs and Steve Wozniak in Los Altos, California. As is legend at this point, the company was started in Jobs’ garage. There, the founders aimed to develop and sell personal computers, with a vision of changing the way the average person viewed home PCs. Their first product, the Apple I, laid the groundwork for future innovations, but it wasn’t until the Apple II’s release that they made a name for themselves with revolutionary color graphics.
After two decades competing with Microsoft in the home computer space, Apple became an unprecedented market leader in the portable MP3 space with the launch of the iPod in 2001. However, it was the creation of the iPhone in 2007 that truly elevated Apple to the great name we know today. Touted as one of the world’s most successful products, the iPhone’s many versions have sold billions of units, and allowed Apple Inc. to become the first company valued at one trillion dollars in 2018. Just two years later, it doubled that figure. Since the historic iPhone launch, Apple has released many new products to various success and increased their reach around the world through their profitable innovations and various company acquisitions.
What Companies Does Apple Own?
Since its beginnings as a home computer manufacturer, Apple has dramatically changed its operations to include a variety of products and services. Apple has acquired approximately 125 companies over its lifetime, many of which are still in operation today. Many of these were smaller companies that Apple incorporated into their products, such as FaceID being created from PrimeSense. PrimeSence was acquired by Apple in 2013.
In 2022, Apple’s CEO Tim Cook claimed Apple had acquired more than 100 companies over the preceding six years alone. Apple subsidiaries are only expected to increase as the brand continues its upward trajectory, though it’s important to note that their acquisition rate has slowed recently with the cooling of the investment in the tech sector since the start of the COVID-19 pandemic.
So far, Apple’s largest acquisition has been Beats at $3 Billion, followed by Intel at $1 Billion.
Apple’s Product Range
Currently, Apple Inc. has five main products: Macs, iPhones, iPads, accessories and services. Over the years, the company has shifted their primary focus from the home computer space in favor of the mobile device market, which has proven to be more lucrative. Though Apple has rarely been the first to introduce a product of its kind to the market, they have a history of redefining the market with their innovations to the field.
Mac
Personal computers have been the foundation of Apple’s product lineup since the beginning with Mac taking the mantle in 1979. Though they still compete with Microsoft in this space, Apple’s M1 and M2 chips have set new standards in the computing industry.
iPhone
In the era of flip phones and BlackBerry, the iPhone revolutionized the mobile phone industry and made smart phones the new global standard. Since then, each new generation of iPhone has introduced significant advancements in camera technology, processing power, and software features, solidifying its status as a market leader.
Apple Watch
The Apple Watch was introduced in 2014 and has quickly become the world’s most popular smartwatch. Combining fitness tracking, health monitoring, and communication features in a sleek, customizable design, it’s carved out a space as a health device as well as a smartphone accessory.
iCloud
iCloud, launched in 2011, is Apple’s cloud storage and computing service, which allows users to store data such as photos, documents, and music, and sync them across all their Apple devices. iCloud has become an integral part of the Apple ecosystem, ensuring seamless data management and providing services like iCloud Drive, iCloud Photos, and iCloud Backup.
Apple Pay
Apple Pay, introduced in 2014, is Apple’s mobile payment and digital wallet service. Thanks to its secure, contactless payments, integrated with the iPhone, Apple Watch, and other Apple devices, it has become a popular choice for digital transactions worldwide.
Who Owns Apple?
Apple’s stock market performance has been nothing short of remarkable. Since it first hit $1 trillion with the launch of the iPod, Apple’s continuous releases, innovations, and success have ranked it among the most valuable companies in the world. The company’s commitment to returning value to shareholders through dividends and stock buybacks further enhances its attractiveness as an investment.
As of January 2024, The Vanguard Group holds the largest percentage of Apple shares at 8.54%. Arthur Levinson, Chairman of the Board, takes the prize for individual shareholders, holding more than 4.5 million shares.
Apple Inc. is a cultural and financial juggernaut that continues to shape the modern world through its creative and strategic vision. From its humble beginnings in a garage to its status as a trillion-dollar company, Apple’s journey is a testament to its ability to adapt and lead. For investors and technology enthusiasts alike, Apple is a fascinating case study in the power of innovation and business strategy. Check out our business visualizations for more on topics like Apple, or take a look at all of the data visualizations on The Chartistry.
List of Companies Apple Owns
- Beats Electronics
- Intel Smartphone Modem Business (include S.M.D. under Intel logo)
- Dialog Semiconductor
- Anobit Technologies
- Texture
- Shazam
- NeXT
- PrimeSense
- AuthenTec
- PA Semi
- Beddit
- Braeburn Capital
- Claris
- Siri
- Mobeewave
Apple Products
| Apple Product | Percent of Company’s Revenue, end of 2023 |
| Mac | 8.00% |
| iPhone | 50%+ |
| iPad | 7.00% |
| Wearables, Home and Accessories | 10.00% |
| Airpods | |
| Apple Watch | |
| Apple TV | |
| Home Pod | |
| Vision Pro | |
| Beats Headphones | |
| Services: | 22.00% |
| App Store (advertising space) | |
| Apple News app (advertising space) | |
| AppleCare+ | |
| iCloud+ | |
| Apple Card | |
| Apple Pay | |
| Apple Books | |
| Apple Fitness+ | |
| Apple Music | |
| Apple News+ | |
| Apple TV+ | |
| Apple Arcade | |
| Apple Podcasts | |
| iTunes Store |
Who Owns Apple?
| # | The 10 Largest Stockholders | Percent of Apple Shares |
| 1 | The Vanguard Group | 8.54% |
| 2 | BlackRock | 6.75% |
| 3 | Berkshire Hathaway | 5.86% |
| 4 | State Street Corporation | 3.80% |
| 5 | Geode Capital Management | 1.95% |
| 6 | Fidelity Investments | 1.94% |
| 7 | Morgan Stanley | 1.41% |
| 8 | T. Rowe Price | 1.37% |
| 9 | Norges Bank | 1.14% |
| 10 | Northern Trust | 1.05% |
Business Visualizations
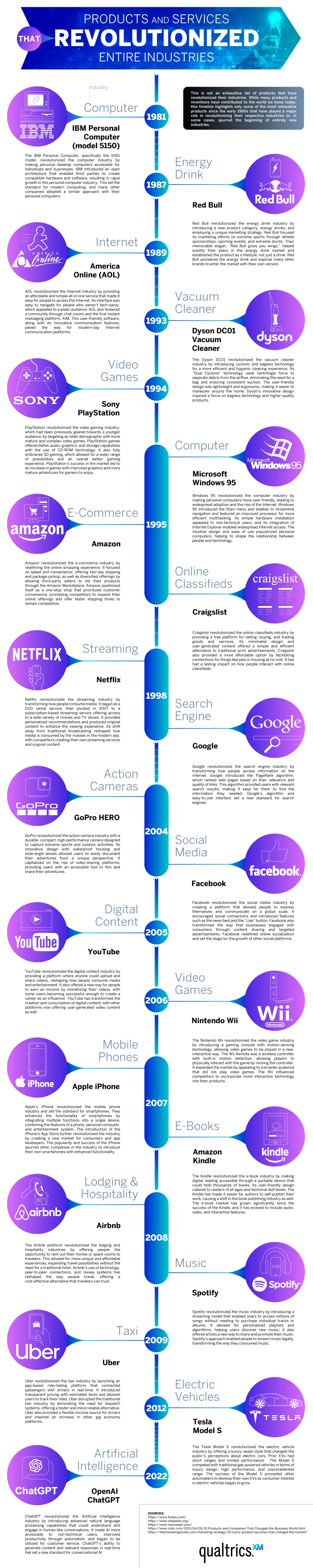
Exploring Technology That Revolutionized Industries
Breakthroughs in technology can revolutionize industries and even give birth to new industries previously unimagined. The Qualtrics team explored the world’s most revolutionary products and services, arranged on a timeline that teaches us not only which tech has caused the biggest changes, but also how these developments interact with each other and advance technology and our lives as a whole. The timeline spans 1981 to 2022. It covers the realms of Computing and Internet, Entertainment and Media, and Mobile and Digital Services. Each item on the timeline has changed its industry and even changed the way humans live.
In the world of computing and Internet services, the timeline covers:
- IBM Personal Computer
- America Online
- Microsoft Windows 95
- Google Search Engine
- OpenAI ChatGPT
Click below to zoom.
The timeline covers the world of entertainment, featuring Sony PlayStation, Amazon, Craigslist, Netflix, Facebook, YouTube, and Nintendo Wii as the gamechangers. In the mobile and digital services realm, there’s a surprising diversity of products from smartphone models to apps like Uber to the Dyson DC01 Vacuum Cleaner, and even Red Bull energy.
It’s no secret that the personal computer revolutionized the business and computing industries. Before IBM’s PC, there was no market for personal computers; today, they’re a staple of modern life. Another 1980s brand, Red Bull, created a market where none previously existed. People traditionally get their caffeine fix from coffee, but energy drinks offer an easier-to-grab option on the go. Red Bull partnered with extreme-sports marketing to turn energy drinks into a lifestyle.
The timeline highlights AOL Instant Messenger as the Internet’s first big revolution. It’s a precursor to social media and helped make the World Wide Web a means of quick, easy communication. In 1998, Google Search Engines made the Internet an invaluable tool for knowledge. Google made it far easier to find websites of value on any topic under the sun (and even some beyond!)
From here on, the timeline is dominated by a range of innovative apps and Internet-based services. Amazon is the worldwide leader in e-commerce. It changed the way consumers shop forever, offering low prices, convenience, and fast delivery. Netflix changed the way people consume films and television by offering the first-ever streaming service. They offer an enormous library of new and old titles. No more waiting for a syndicated show to air. Netflix created a demand for “binge-worthy” content. The entertainment world touches every area of traditional arts and media. We see the Amazon Kindle changing how many book lovers read, offering a digital library that saves physical space and even money for some titles. Spotify became the leader of music streaming in 2008. Some think of it as the Netflix of music. Memberships offer unlimited streaming access to millions of songs and artists.
These are just a few of the industries that have been revolutionized by technology. We haven’t even touched on AI! Dive into the timeline to learn more about the most pivotal products and services of the modern era.
Business Visualizations
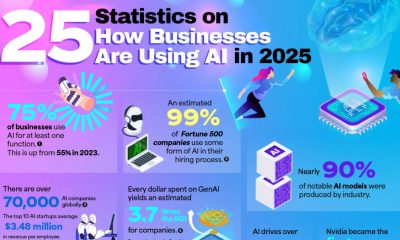
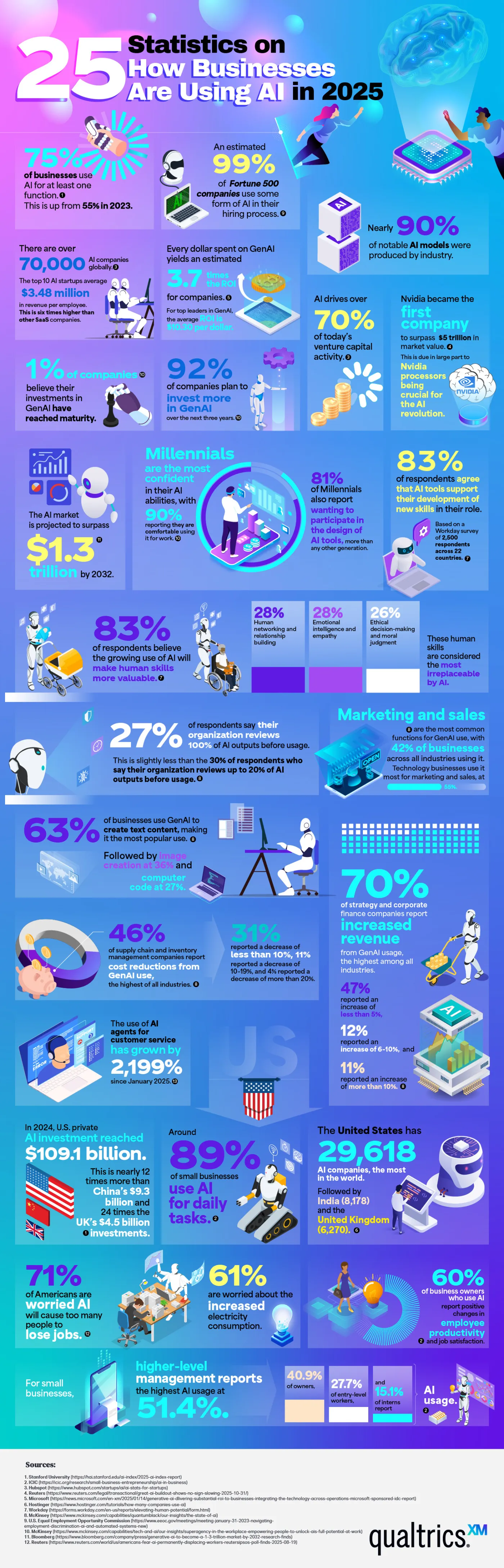
Statistics Are the Key to Understanding AI’s Influence on Business
“Artificial intelligence” may be the biggest buzzword of 2026. It seems like every industry is incorporating AI into its practices, but it has had the biggest impact in the business sector. Nearly 80% of businesses use AI in some way. Qualtrics has quantified the massive impact AI has on business with a chart listing 25 key statistics that illustrate its influence. These statistics help us understand how and why businesses are using AI to reach the next level.
Many of the statistics listed show why businesses are so drawn to AI. In 2025, three out of four companies used AI regularly for at least one task. 99% of Fortune 500 companies use AI in their hiring process to screen applicants for predicted success in a role. 83% of business professionals say they’re using AI to learn new skills to further their career. Perhaps the most compelling reason businesses turn to AI is their profits. Every dollar invested in generative AI yields an average return of $3.70. Businesses are embracing what they see as AI’s stronger performance and competitive edge.
There is no doubt that AI is profitable, as these figures show. 70% of companies report increased revenue that they attribute to generative AI. Supply chains use AI to streamline logistics, and on the marketing side of business, 42% report using AI for content generation. Customer service has seen a huge explosion in AI usage, almost a 2000% increase.
AI has strong momentum, with about 70,000 companies using it globally. U.S. private investment in AI is around $109.1 billion. 90% of the world’s AI models are the work of private industry rather than government-funded research or academia, highlighting that business not only uses AI but also fuels its creation.
Small businesses are a part of these statistics. 89% of small businesses use AI in their daily operations, often for financial management and customer service. 60% of small business owners say AI has improved their employees’ productivity. Executives and senior managers are the most avid users of AI, but use by interns and entry-level employees rises every year.
Here are a few other jaw-dropping statistics that show how enormous a presence AI has in the business industry:
- AI drives over 70% of venture capital activity.
- 92% of companies plan to invest more in AI within the next three years.
- 63% of businesses use AI to generate text-based content.
- The use of AI customer service agents has grown by 2,199% since January.
- The United States is home to 29,618 AI companies, which is more than any other country.
These statistics underscore that AI is becoming a regular part of everyday business practices. Companies often say they believe AI amplifies their employee’s natural talents. Whether used for strategy, customer service, or content generation, it seems AI is here to stay.
Business Visualizations
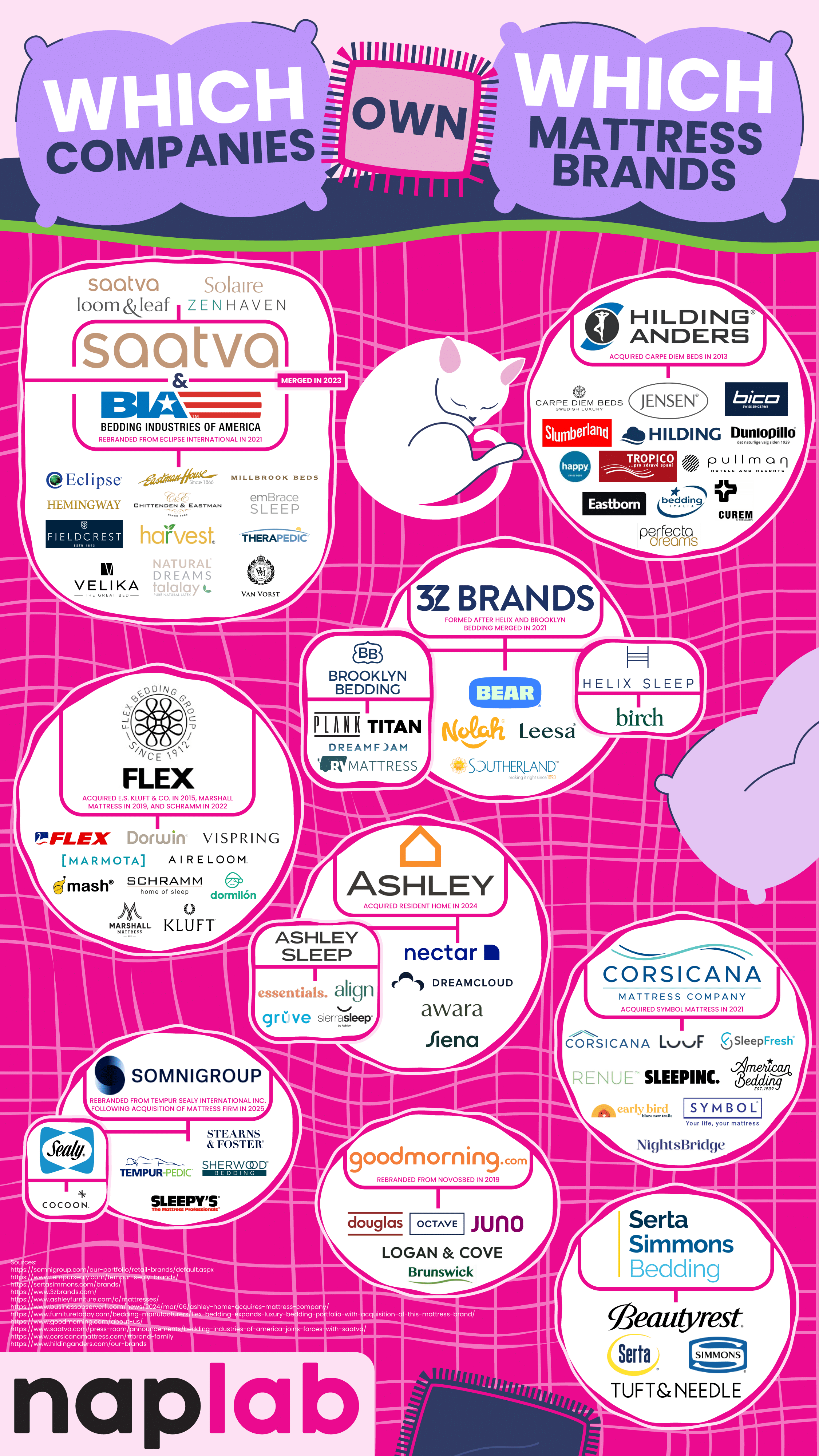
Most Mattress Brands Are Owned by a Handful of Companies
When you visit a mattress store or browse through mattress options online, there are a lot of choices that make us feel like we’re choosing from dozens of options from a wide variety of companies. But this choice is an illusion, as a handful of corporations actually own these brands and control large portions of the mattress and bedding industries. The team at NapLab breaks down ownership of the most recognizable mattress companies. Their work shows us that brand diversity is often a mask for a limited corporate structure.
Click below to zoom.
One of the biggest shareholders of the mattress industry is Somnigroup International. They used be called Tempur Sealy International, a name you probably recognize. What you might not realize is that this company owns brands like Tempur-Pedic, Sealy, Stearns & Foster, Sherwood Bedding, and Sleepy’s. They also own the entire extensive Mattress Firm retail store network. This makes Somnigroup International a powerful driving force in mattress sales and distribution.
Another big player in the industry is Serta Simmons Bedding LLC (SSB). They own classic brand names like Simmons, Serta, Beautyrest, and Tuft & Needle. SSB has had its share of financial challenges, including filing for Chapter 11 bankruptcy in 2023, but it still continues to own a significant share of the American mattress market.
Not all these owners are giant manufacturers. Ashley Global Retail is best known for furniture, but it entered the mattress market when it acquired the Resident Home family of brands, which includes Nectar, Awara, Siena, DreamCloud, and Ashley Sleep. These options encompass both luxury and budget-friendly mattress brands.
3Z Brands is a key player in the direct-to-consumer mattress sales space. They own the brands Helix Sleep, Bear, Brooklyn Bedding, Leesa, and Nolah. These brands represent the share of shoppers who prefer buying a mattress online rather than dealing with retailers and sales representatives.
Saatva Inc. used to focus solely on selling luxury mattresses online, but in 2023, it merged with Bedding Industries of America. The merger added other brands to their roster, including Eclipse, Millbrook, Ernest Hemingway, and Eastman House, in addition to Saatva’s name brand of products.
We also see some international companies represented here. GoodMorning.com, formerly known as Novosbed, is a Canadian company that primarily sells to the U.S. market, encompassing the brands Octave, Juno, Douglas, and Logan & Cove.
The Flex Bedding Group is Spanish-owned and sells luxury and niche products to Americans, including the high-end brands Marshall Mattress, E.S. Kluft & Co., Kluft, Aireloom, and Vispring.
Understanding which companies own these mattress brands helps consumers make informed choices. It also helps us understand that brands might appear vastly different, but in reality, they’re under the same corporate umbrella, which influences everything from pricing to marketing to manufacturing.
This brand consolidation isn’t any different from many other industries, like beer and skincare, but it does raise consumer concerns about true choice and industry competition.
-

 Business Visualizations1 year ago
Business Visualizations1 year agoAmerica’s Most Valuable Companies Ranked by Profit per Employee
-
 Business Visualizations1 year ago
Business Visualizations1 year agoThe Biggest Fortune 500 Company in Every State
-

 Business Visualizations10 months ago
Business Visualizations10 months agoThe Biggest Employers by Industry
-
 Business Visualizations2 years ago
Business Visualizations2 years agoNew Animated Map Shows Airbnb’s Fully Booked Cities Along the 2024 Eclipse Path of Totality
-

 Business Visualizations2 years ago
Business Visualizations2 years agoEverything the Luxury Giant LVMH Owns in One Chart
-
 Timelines1 year ago
Timelines1 year agoTimeline Charts the Development of Communications Technology
-

 Charts2 years ago
Charts2 years agoHow Many Crayola Crayon Colors Are There? A Lot.
-

 Business Visualizations5 months ago
Business Visualizations5 months agoThe Largest Companies in America That Are Still Run by the Person Who Founded Them