Business Visualizations
The Biggest Employers by Industry
There are more than 30 million businesses in the U.S. — but some of those companies employ far more workers than others. Giants like Walmart and Amazon have more than a million employees working on developing, marketing, transporting and selling their products everyday. Meanwhile, lesser-known companies in industries you may not be as familiar with also employ a significant amount of our workforce.
Using Fortune 500 data, our team at The Chartistry identified the largest employers in every industry, including retail, food, health care, real estate and many more (we included a whopping 75 industries total).
Click below to zoom
Who is the largest employer in America?
Technically, the largest employer in the U.S. is the federal government. But if we’re talking about the company that employs the most people, Walmart takes the cake.
Since Walmart’s first store opened in 1962, the company has grown to establish more than 11,500 stores globally to serve more than 260 million weekly shoppers in 28 countries, according to the company’s site. It’s no surprise that the retailer requires a lot of manpower. Walmart has 2,100,000 employees, and is the only one on our list that employs more than 2 million people.
Who else are America’s biggest employers?
Walmart may offer up the most jobs in the U.S.,but there are plenty of other companies with thousands of employees headed to work everyday. Some of the giants on the list of companies with the most employees in every industry are also among the largest U.S. employers in general.
Amazon, which started in Jeff Bezos’ garage in 1994 as an online bookseller, has grown up to make its mark around the world. There’s a good chance you’ve shopped online via the company, watched its streamer or walked past an Amazon retail store or fulfillment center. Amazon may have started with a solo founder, but it now employs 1,525,000 people.
Home Depot is another retail heavyweight. Founded in 1978 as a hardware store, the company now boasts more than 2,300 stores across North America. But offering up all that home improvement requires a lot of hands on deck: The company has 463,100 employees. That makes it the highest employer in one category of specialty retailers, but TJX, with 349,000 employees, is the largest employer in the apparel-specific specialty retailer category.
In the mail, package and freight delivery industry, you can probably guess who employs the most people. It’s FedEx, which was just an idea in 1965 when its eventual founder Frederick W. Smith wrote a paper at Yale University on the potential of a new way to get time-sensitive shipments to recipients (he received an average grade, according to the company’s website). Since then, the company makes around 14.5 million deliveries each day thanks to its 446,400 employees.
UnitedHealth Group also made our list, which makes sense, seeing as its the largest health insurance company in the U.S. Parent company of United Healthcare, the company was founded in 1977. Nowadays, it employs 440,000 people.
Curious which food and drug store is the largest employer? That would be Kroger, which had its start in 1883 when Barney Kroger invested his life savings of $372 to open a single grocery store. More than 140 years later, Kroger is the nation’s largest grocer with nearly 2,800 stores in 35 states and 414,000 employees. But if we’re talking specifically about food services, latte lovers’ favorite place, Starbucks, is the largest employer, with 381,000 employees. Looking specifically at the food consumer products industry, PepsiCo — which owns brands like Lay’s, Doritos, Gatorade, Quaker and, of course, Pepsi — is the largest employer with 318,000 employees.
The travel industry also requires tons of workers. American Airlines Group, which offers thousands of flights daily in more than 60 countries, is the largest employer in the airline industry with 132,100 people. Hilton Worldwide Holdings, meanwhile, has 178,000 employees to help run its hotels, casinos and resorts.
In the entertainment industry, a very familiar name earns the title for largest employer with its 199,125 workers: Walt Disney.
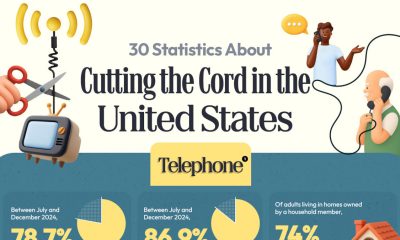
The largest U.S. employers in each industry
Here are the largest companies by employees in every industry — from hotels and airlines to pharmaceuticals and medical equipment.
|
Industry |
Company |
Number of Employees |
|
General Merchandisers |
Walmart |
2,100,000 |
|
Internet Services and Retailing |
Amazon |
1,525,000 |
|
Specialty Retailers: Other |
Home Depot |
463,100 |
|
Mail, Package, and Freight Delivery |
FedEx |
446,400 |
|
Health Care: Insurance and Managed Care |
UnitedHealth Group |
440,000 |
|
Information Technology Services |
Concentrix |
440,000 |
|
Food and Drug Stores |
Kroger |
414,000 |
|
Insurance: Property and Casualty (Stock) |
Berkshire Hathaway |
396,500 |
|
Food Services |
Starbucks |
381,000 |
|
Specialty Retailers: Apparel |
TJX |
349,000 |
|
Food Consumer Products |
PepsiCo |
318,000 |
|
Commercial Banks |
JPMorganChase |
309,926 |
|
Health Care: Medical Facilities |
HCA Healthcare |
265,000 |
|
Diversified Outsourcing Services |
Aramark |
262,550 |
|
Health Care: Pharmacy and Other Services |
CVS Health |
259,500 |
|
Semiconductors and Other Electronic Components Equipment |
Jabil |
236,000 |
|
Computer Software |
Microsoft |
221,000 |
|
Entertainment |
Walt Disney |
199,125 |
|
Motor Vehicles & Parts |
Lear |
186,600 |
|
Telecommunications |
Comcast |
186,000 |
|
Aerospace & Defense |
RTX |
185,000 |
|
Hotels, Casinos, Resorts |
Hilton Worldwide Holdings |
178,000 |
|
Computers, Office Equipment |
Apple |
161,000 |
|
Food Production |
Tyson Foods |
139,000 |
|
Airlines |
American Airlines Group |
132,100 |
|
Pharmaceuticals |
Johnson & Johnson |
131,900 |
|
Real Estate |
CBRE Group |
130,000 |
|
Industrial Machinery |
General Electric |
125,000 |
|
Scientific, Photographic, and Control Equipment |
Thermo Fisher Scientific |
122,000 |
|
Medical Products and Equipment |
Abbott Laboratories |
114,000 |
|
Construction and Farm Machinery |
Caterpillar |
113,200 |
|
Transportation and Logistics |
GXO Logistics |
109,000 |
|
Household and Personal Products |
Procter & Gamble |
107,000 |
|
Network and Other Communications Equipment |
Amphenol |
95,000 |
|
Chemicals |
3M |
85,000 |
|
Diversified Financials |
Marsh & McLennan |
85,000 |
|
Apparel |
Nike |
83,700 |
|
Tobacco |
Philip Morris International |
82,700 |
|
Beverages |
Coca-Cola |
79,100 |
|
Advertising, Marketing |
Omnicom Group |
75,900 |
|
Wholesalers: Food and Grocery |
Sysco |
71,750 |
|
Insurance: Property and Casualty (Mutual) |
State Farm Insurance |
65,054 |
|
Petroleum Refining |
Exxon Mobil |
61,500 |
|
Financial Data Services |
Fidelity National Information Services |
60,000 |
|
Wholesalers: Diversified |
Genuine Parts |
60,000 |
|
Electronics, Electrical Equipment |
Whirlpool |
59,000 |
|
Oil And Gas Equipment, Services |
Baker Hughes |
58,000 |
|
Packaging And Containers |
WestRock |
56,100 |
|
Securities |
Edward Jones |
54,000 |
|
Engineering and Construction |
Quanta Services |
52,500 |
|
Home Equipment, Furnishings |
Stanley Black & Decker |
50,500 |
|
Waste Management |
Waste Management |
48,000 |
|
Wholesalers: Health Care |
McKesson |
48,000 |
|
Insurance: Life, Health (Stock) |
MetLife |
45,000 |
|
Trucking, Truck Leasing |
J.B. Hunt Transport Services |
34,718 |
|
Toys, Sporting Goods |
Mattel |
33,000 |
|
Railroads |
Union Pacific |
32,973 |
|
Metals |
Nucor |
32,000 |
|
Automotive Retailing, Services |
CarMax |
30,621 |
|
Building Materials, Glass |
Builders FirstSource |
29,000 |
|
Utilities: Gas and Electric |
PG&E |
28,010 |
|
Wholesalers: Electronics and Office Equipment |
TD Synnex |
28,000 |
|
Temporary Help |
Manpower Group |
27,900 |
|
Mining, Crude-Oil Production |
Freeport-McMoRan |
27,200 |
|
Equipment Leasing |
United Rentals |
26,300 |
|
Publishing, Printing |
News Corp. |
25,000 |
|
Miscellaneous |
Service Corporation International |
21,267 |
|
Transportation Equipment |
Polaris |
18,500 |
|
Energy |
NRG Energy |
18,131 |
|
Education |
Graham Holdings |
17,006 |
|
Insurance: Life, Health (Mutual) |
TIAA |
16,023 |
|
Pipelines |
Energy Transfer |
13,786 |
|
Homebuilders |
D.R. Horton |
13,450 |
|
Forest and Paper Products |
Domtar |
13,000 |
|
Shipping |
Kirby Corporation |
5,450 |
Don’t miss our other visuals (Chartistry Originals) that give insight into some of the biggest employers in the U.S, including our map of the biggest Fortune 500 companies in every state, breakdown of America’s most valuable companies ranked by profit per employee and original chart of everything owned by Apple.
Source:
Business Visualizations
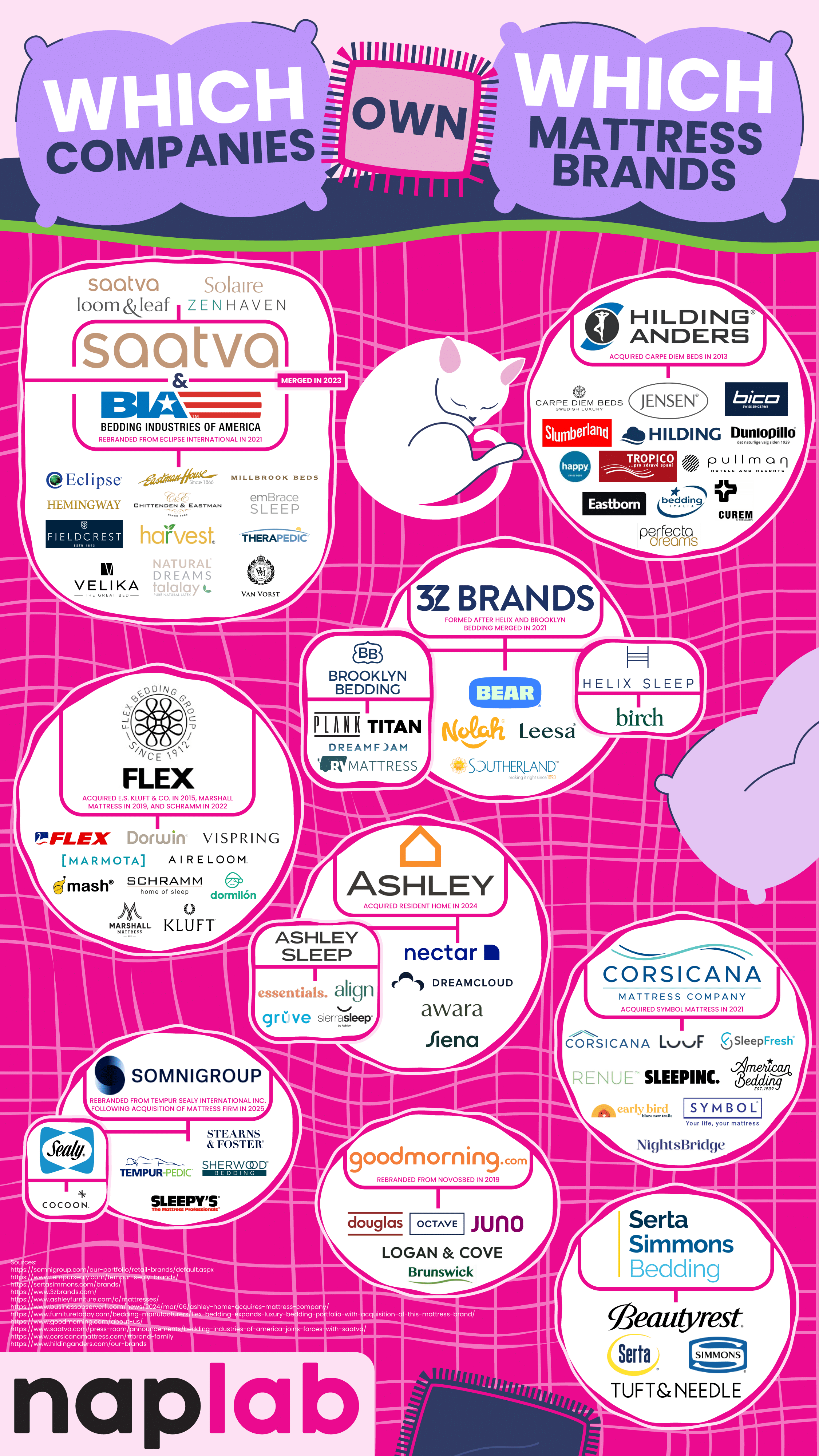
Most Mattress Brands Are Owned by a Handful of Companies
When you visit a mattress store or browse through mattress options online, there are a lot of choices that make us feel like we’re choosing from dozens of options from a wide variety of companies. But this choice is an illusion, as a handful of corporations actually own these brands and control large portions of the mattress and bedding industries. The team at NapLab breaks down ownership of the most recognizable mattress companies. Their work shows us that brand diversity is often a mask for a limited corporate structure.
Click below to zoom.
One of the biggest shareholders of the mattress industry is Somnigroup International. They used be called Tempur Sealy International, a name you probably recognize. What you might not realize is that this company owns brands like Tempur-Pedic, Sealy, Stearns & Foster, Sherwood Bedding, and Sleepy’s. They also own the entire extensive Mattress Firm retail store network. This makes Somnigroup International a powerful driving force in mattress sales and distribution.
Another big player in the industry is Serta Simmons Bedding LLC (SSB). They own classic brand names like Simmons, Serta, Beautyrest, and Tuft & Needle. SSB has had its share of financial challenges, including filing for Chapter 11 bankruptcy in 2023, but it still continues to own a significant share of the American mattress market.
Not all these owners are giant manufacturers. Ashley Global Retail is best known for furniture, but it entered the mattress market when it acquired the Resident Home family of brands, which includes Nectar, Awara, Siena, DreamCloud, and Ashley Sleep. These options encompass both luxury and budget-friendly mattress brands.
3Z Brands is a key player in the direct-to-consumer mattress sales space. They own the brands Helix Sleep, Bear, Brooklyn Bedding, Leesa, and Nolah. These brands represent the share of shoppers who prefer buying a mattress online rather than dealing with retailers and sales representatives.
Saatva Inc. used to focus solely on selling luxury mattresses online, but in 2023, it merged with Bedding Industries of America. The merger added other brands to their roster, including Eclipse, Millbrook, Ernest Hemingway, and Eastman House, in addition to Saatva’s name brand of products.
We also see some international companies represented here. GoodMorning.com, formerly known as Novosbed, is a Canadian company that primarily sells to the U.S. market, encompassing the brands Octave, Juno, Douglas, and Logan & Cove.
The Flex Bedding Group is Spanish-owned and sells luxury and niche products to Americans, including the high-end brands Marshall Mattress, E.S. Kluft & Co., Kluft, Aireloom, and Vispring.
Understanding which companies own these mattress brands helps consumers make informed choices. It also helps us understand that brands might appear vastly different, but in reality, they’re under the same corporate umbrella, which influences everything from pricing to marketing to manufacturing.
This brand consolidation isn’t any different from many other industries, like beer and skincare, but it does raise consumer concerns about true choice and industry competition.
Business Visualizations
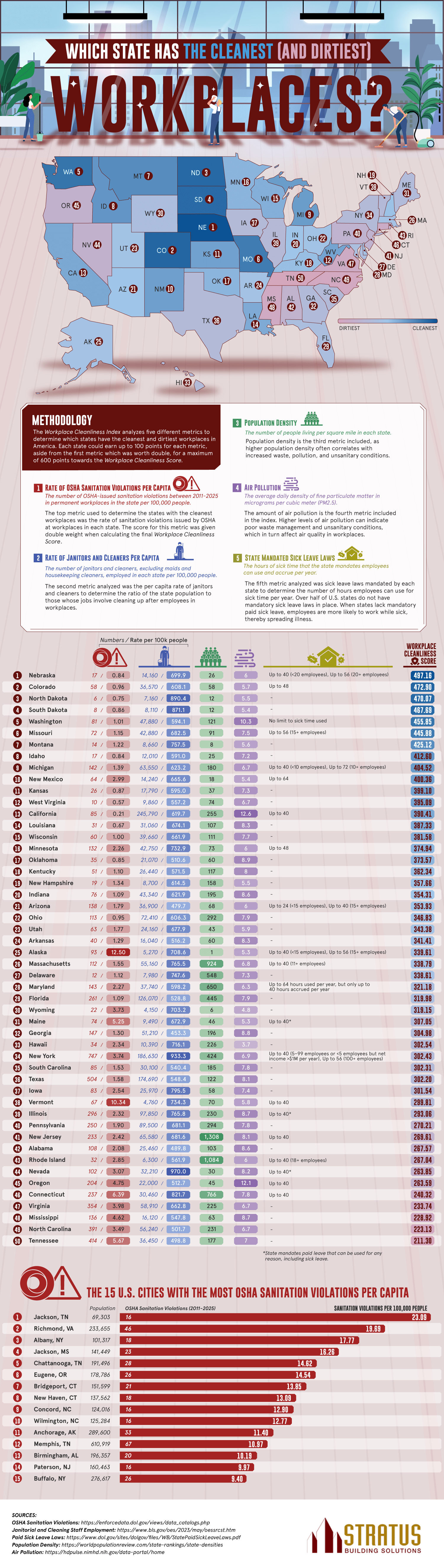
Ranking States by Workplace Cleanliness
The team at Stratus Building Solutions reveals which states have the cleanest and dirtiest workplaces in a new study. Cleanliness is often an overlooked but powerful influence on workers’ health, happiness, and productivity. People who work in an office spend many hours there and have a right to a clean, safe space to work, whether that’s at their desk, in the breakroom, or in the bathroom. The team’s study reveals that cleanliness depends on more than company policy and culture. It’s impacted by resources and state laws. While some states mandate rules that boost workers’ health and safety, other locations lack such protections and put workers at risk.
Click below to zoom.
The team created a scoring system based on some key criteria. First was the number of OSHA violations. OSHA is the Occupational Safety and Health Administration, which sets federal workplace safety standards, including sanitation standards. A state with a high number of OSHA sanitation violations is a clear sign of dirty workplaces. These violations could include unclean restrooms, inadequate waste disposal, or the presence of mold and bacteria. The team also examined the number of janitors per capita, population density, air pollution, and sick leave laws in each state.
The team found that these states were the cleanest with the highest scores:
- Nebraska
- Colorado
- North Dakota
- South Dakota
- Washington
- Missouri
- Montana
- Idaho
- Michigan
- New Mexico
The top scorers had low rates of OSHA violations, clean air, and high janitor-to-population ratios. State laws mandating sick leave also play a major role, as workers are more likely to stay home rather than bring germs to work.
These were the states that struggled the most with these standards:
- Tennessee
- North Carolina
- Mississippi
- Virginia
- Connecticut
- Oregon
- Nevada
- Rhode Island
- Alabama
- New Jersey
- Pennsylvania
Many of these states are on the dirty end of the spectrum, lacking paid sick leave. Tennessee, Mississippi, and North Carolina do not have laws on paid sick leave, which, when combined with the absence of handwashing stations and disinfecting services, makes the workplace a petri dish for germs. We also see heavily populated states like New York and New Jersey on the low end of the spectrum because more people means a greater challenge to clean up waste and keep germs at bay. High populations also mean bigger cities and more air pollution. We do see, however, that lower population density doesn’t necessarily mean cleaner workplaces, as Vermont was near the bottom of the list and has a small population.
Clean workplaces are healthy workplaces. Dust, germs, and air pollution lead to gastrointestinal and respiratory problems among workers. Simple precautions like regularly disinfecting surfaces, installing handwashing stations, and removing dust can boost the cleanliness of the office and the health of workers. Healthy workers mean better productivity and greater safety for all. Not only will a clean space improve worker experience, but OSHA violations can be very costly. The team’s study provides fascinating insights into what affects workplace cleanliness.
Business Visualizations
New Study Examines Language Used to Let Employees Go
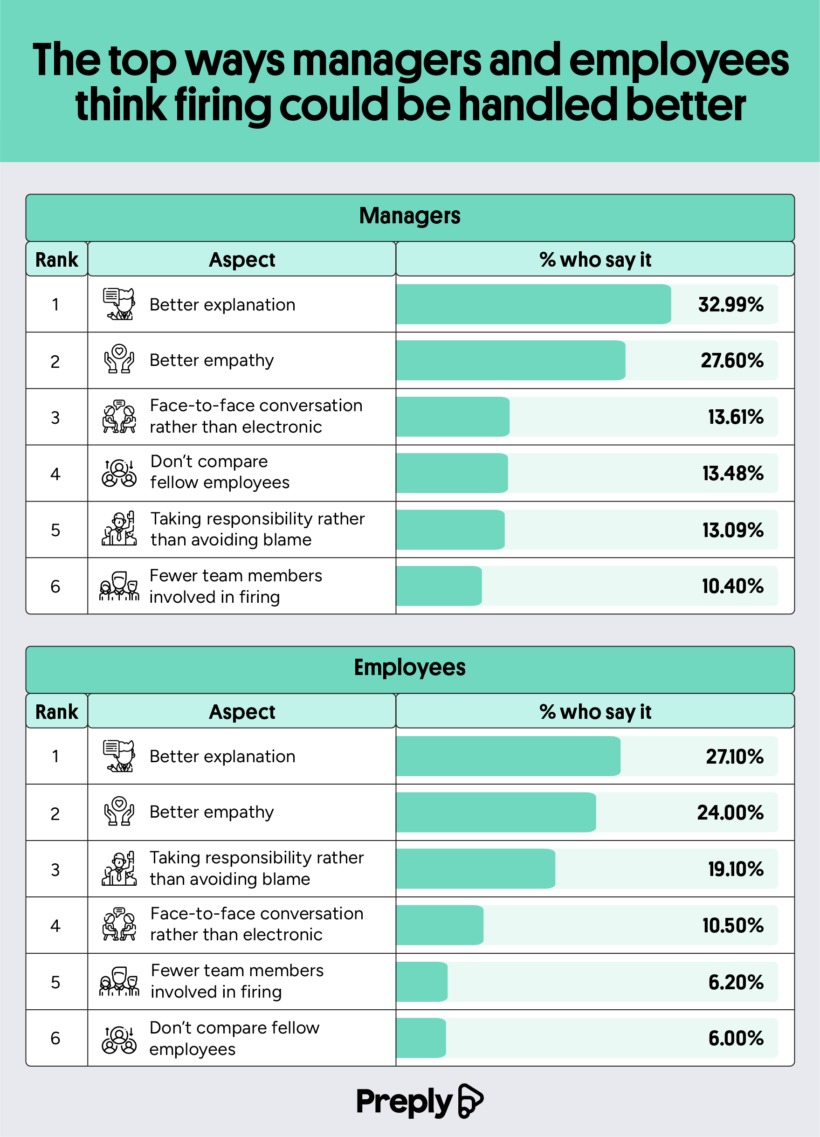
Letting an employee go is an unpleasant experience for everyone involved, but language has the power to guide the emotions surrounding an interaction. While the right words won’t erase the bad side of being let go, they can help the employee in question understand why the situation is happening and make them feel seen and heard. Preply leaned into the language aspects in these situations with a study examining the most common phrases and words used when letting an employee go and how employers and employees felt about the situation.
Click below to zoom.
Overall, the team found that these were the most common phrases used:
- Letting you go
- Effective immediately
- Terminating your employment
- This isn’t working out
- No longer require services
- Parting ways
- Ending your employment
- No longer needed
- Relieved of duties
- Ending our working relationship
Managers and employees seem to agree that lack of empathy and responsibility were the most common complaints about the process. One in six managers say they regret the words they chose when firing someone, and 92% feel they need more training on how to handle such situations. Employees wanted their managers to focus on clarity, compassion, empathy, and honesty when firing an employee.
The team studied changes that both managers and employees would like to see in the firing process.
These are the six things employees want to see improved:
- Better explanation
- Better empathy
- Taking responsibility rather than avoiding blame
- Face-to-face conversation rather than electronic
- Fewer team members involved in the firing
- Don’t compare fellow employees
Here’s how that compares to changes managers would like to make to the process:
- Better explanation
- Better empathy
- Face-to-face conversation rather than electronic
- Don’t compare fellow employees
- Taking responsibility rather than avoiding blame
- Fewer team members involved in firing
These are similar answers, but we can see that the two groups ranked their importance differently. Overall, 92% of Americans think managers could benefit from some language training when it comes to firing someone. Empathy and honesty were high on the list of employee wishes, indicating that understanding can help give them closure on the job, and empathy softens the blow. Not many managers would prefer a face-to-face meeting. Only 1 in 6 prefer this to virtual meetings, which seem to be the most common option.
Only 55% of managers have received training on how to fire someone, and with many of them regretting their language choices, it seems that many managers would benefit from some education in business language and communication. Notice that many of the top phrases are more professional ways to say “fired,” like “letting you go,” “terminating,” and “no longer require.”
When managing a team, empathy and clear language are crucial. These skills can help managers excel at many tasks beyond having to let an employee go. But when a situation like firing someone is emotionally charged, the language used becomes more important than ever. Hopefully, the team’s study can help managers reflect on how they go about the process.
-

 Business Visualizations1 year ago
Business Visualizations1 year agoEverything Owned by Apple
-

 Business Visualizations1 year ago
Business Visualizations1 year agoAmerica’s Most Valuable Companies Ranked by Profit per Employee
-
 Business Visualizations11 months ago
Business Visualizations11 months agoThe Biggest Fortune 500 Company in Every State
-
 Business Visualizations2 years ago
Business Visualizations2 years agoNew Animated Map Shows Airbnb’s Fully Booked Cities Along the 2024 Eclipse Path of Totality
-

 Business Visualizations2 years ago
Business Visualizations2 years agoEverything the Luxury Giant LVMH Owns in One Chart
-
 Business Visualizations2 years ago
Business Visualizations2 years agoTimeline Shows the Top 10 Most-Visited Websites Each Year Since 1995
-
 Timelines1 year ago
Timelines1 year agoTimeline Charts the Development of Communications Technology
-

 Charts2 years ago
Charts2 years agoHow Many Crayola Crayon Colors Are There? A Lot.