Charts
New Study Gives a Close Look at Global Waste and Recycling
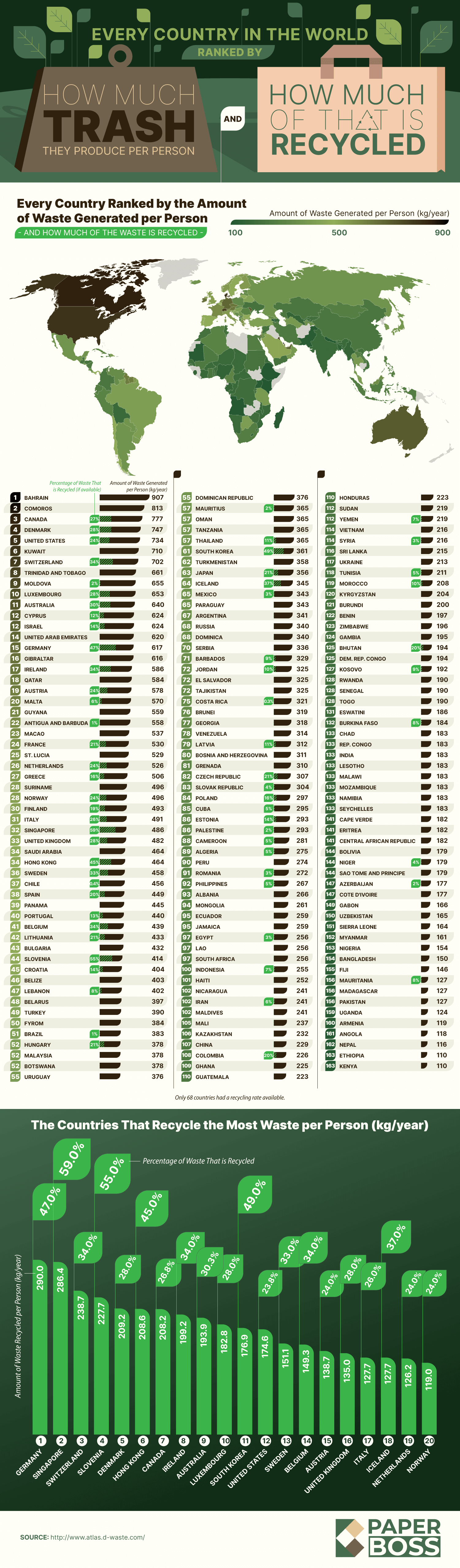
A study by Paper Boss sheds light on the countries generating the most garbage per person, revealing critical insights into global waste production and recycling efforts. The top 10 waste-producing nations are Bahrain, Comoros, Canada, Denmark, the U.S., Kuwait, Switzerland, Trinidad and Tobago, Moldova, and Luxembourg.
Click below to zoom.
Bahrain, despite its small size, leads the list with 907 kilograms of waste per person annually. Rapid population growth and high levels of construction and industrial activity contribute significantly to this figure. Canada, ranking third with 777 kilograms of waste per person, offsets some of its impact by recycling 27% of its trash.
Germany stands out as the global leader in recycling, with an impressive 47% recycling rate. This success stems from a well-established culture of sustainability, where children are taught to separate waste from an early age. Strict regulations, including fines for failing to recycle, further reinforce this commitment.
Interestingly, nations like Switzerland, Denmark, and Luxembourg appear on both the highest waste-producing and top-recycling lists, reflecting a complex balance between consumption and sustainability efforts.
The study underscores the pressing need to address rising waste levels worldwide. Countries like Germany demonstrate how prioritizing education, infrastructure, and accountability can lead to more sustainable practices. By adopting such strategies, other nations could work toward effectively reducing their environmental footprint and combating the global waste crisis.
Charts
New Map Shows Where Americans Spend the Most Time at Home
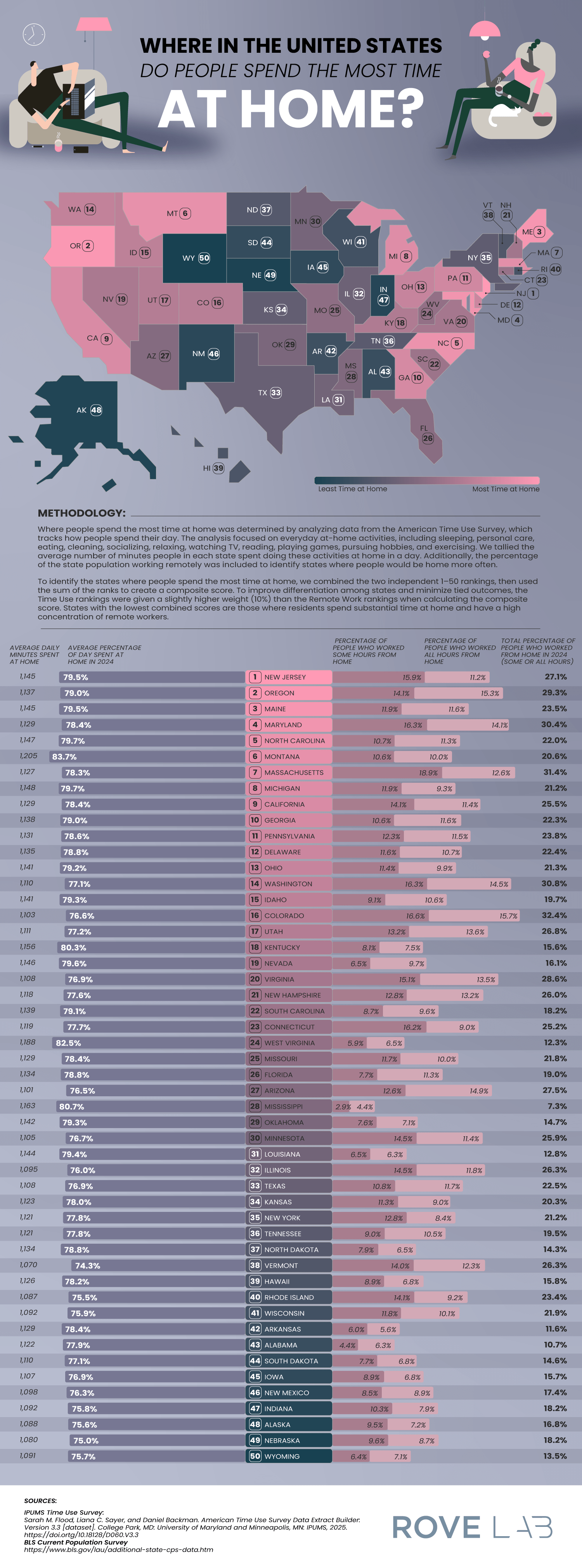
A new article from RoveLab presents a data-driven exploration of home-life habits in the United States, examining how much time Americans spend at home and how that changes across each state. Drawing on data from the American Time Use Survey and the Integrated Public Use Microdata Series, the study constructs a ranking of states based on how much time residents spend at home. This data combined at-home activity levels with remote work prevalence.
RoveLab situates its analysis within broader behavioral shifts in the American lifestyle. On average, Americans spend around 18 hours per day at home (including sleep), which reflects a gradual decline in time spent outside the home over the past two decades. This trend pre-dates the COVID-19 pandemic, which spiked time spent at home and prompted the rise of remote work.
Click below to zoom.
Other important facts on time spent at home add more context:
- 80% of Americans engage in daily household activities like cleaning, cooking, and home maintenance.
- 94% of Americans participate in leisure activities at home, including gaming, socializing, and exercise.
- Most Americans watch about 3.57 hours of television daily, which is more than the average amount of daily time spent on household tasks.
These statistics show that a home is the central site of both productivity and leisure, underscoring the growing connection between work and private life.
To determine which state residents are the most homelife-centric, the researchers developed a scoring system that incorporated:
- Average percentage of the day spent at home
- Average daily minutes spent at home
- Percentage of residents working remotely
- Weighted ranking emphasizing time-use data slightly more than remote work numbers
This multi-factor approach shows the team’s effort to balance behavioral statistics with labor trends, offering a comprehensive view of domestic time use.
The team found that residents in these states spend the most time at home:
- New Jersey: 5% of the day is spent at home (1,1495 minutes) and 27.1% of residents work remotely.
- Oregon: 79% of the day is spent at home and 29.3% of residents work remotely.
- Maine: 79% of the day is spent at home and 23.5% of residents work remotely.
New Jersey’s lead position is due to several structural factors, such as its proximity to major employment centers and a highly educated workforce, with over 40% of residents holding a bachelor’s degree. These factors create a population ideal for telecommuting. It shows us that socioeconomic factors can shape our daily routines.
At the low end of the scoring, Wyoming ranks as the state where people spend the least amount of time at home. This reflects a low rate of remote work. Montana relies on industries like agriculture, mining, and tourism, which all require in-person workers. The team also speculates that Wyoming’s emphasis on outdoor recreation leads residents to both work and play outside their homes.
By combining time-use data with employment patterns, the study provides valuable insight into how regional differences, evolving job requirements, and leisure habits shape modern American life.
Charts
What Percentage Do Popular Side-Gig Apps Take from Each Sale in the U.S.?
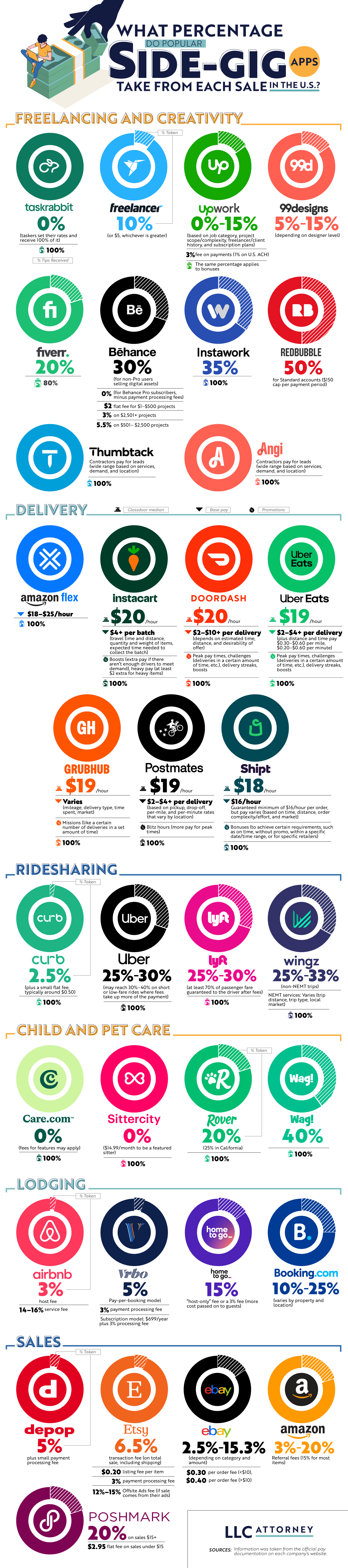
An article from LLC Attorney.com offers one of the most detailed, data-rich comparisons of how much major gig and marketplace platforms extract in fees from workers’ earnings versus how much the workers keep. This article goes beyond anecdotal evidence and offers practical insights alongside raw data. Every freelancer, business owner, and part-time gig worker should understand the information presented here so they can wisely choose where to sell their products and services.
Click below to zoom.
The article’s most important message is that platforms vary widely in how much they take from earnings. These differences can have a big impact on the workers’ bottom line. Here are some examples:
Rideshare Apps: Major platforms like Lyft and Uber typically take about 25% to 30% of passenger fares, and in some cases more for low-priced trips. Drivers do get to keep 100% of tips.
Delivery Services: Delivery gig earnings are reported as base pay plus tips. Workers receive the full tip amount, but pay varies by platform and market demands.
Creative Marketplaces: Platforms like Etsy charge a 6.5% transaction fee on their total sale price, plus a payment processing fee of around 3%. There are also optional advertising fees, so the total fee is about 10%. Poshmark takes 20% of sales over $15.
Pet Care Apps: Some pet care apps, like Rover, take about 20% of earnings in fees, while Wag takes a significantly higher portion, around 40%.
The article also discussed lodging and rental platforms. Hosts on Airbnb pay a 3% host service fee, plus a guest service fee of approximately 14% to 15%. Platforms like Vrbo and Booking.com have variable fee structures that usually land between 10% and 25%, depending on the model.
What makes this article especially useful is the visual chart, which lets you quickly peruse and compare dozens of apps. If a worker juggles multiple platforms, let’s say they’re a DoorDash delivery driver, have an Etsy shop, and flip items on Poshmark, they can compare all these platforms quickly and decide which are the most profitable. This is also crucial information to help people set prices effectively.
The article places these fees in the context of the gig economy boom. Millions of people supplement their income and build independent businesses using these apps. About 16.6% of side hustlers report delivery or ride-sharing gig work as their part-time side hustle, with an online shop and freelancing close behind. Recent surveys show that 70% of Americans earn extra cash through side gigs, often via the apps listed in the chart. Even so, many users underestimate the extent of platforms’ control over visibility, fees, and pricing.
Understanding each platform’s fee structures is integral to a financial platform. These fees and the pricing workers set can have a strong influence on whether a side hustle is profitable. The information presented here is a decision-making tool that combines clear, comparative data with important context to help side hustlers succeed in their ventures.
Charts
Highlighting 30 Safety Features Every Senior Should Know
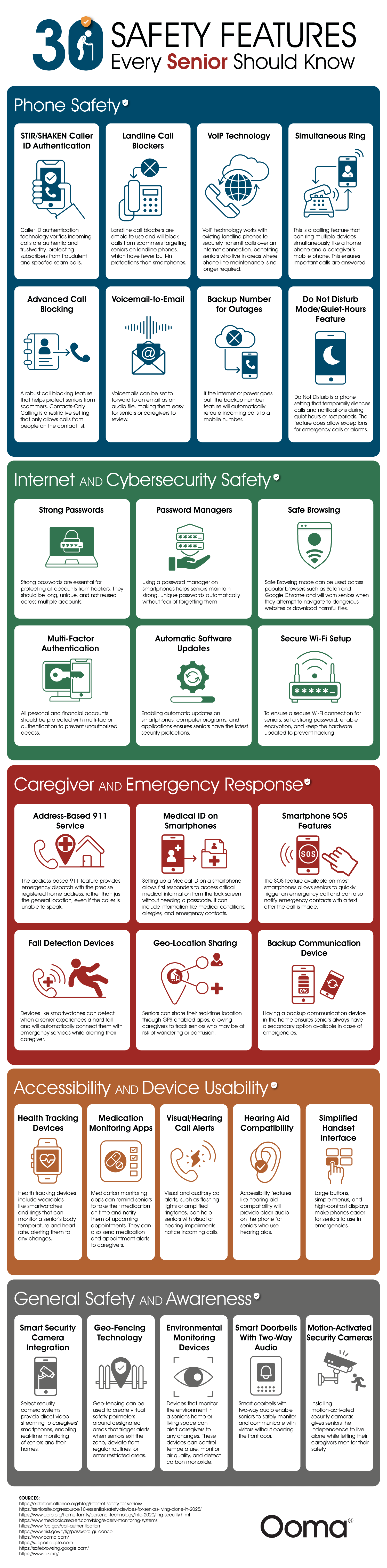
While aging can bring positive life changes, such as retirement and the freedom to spend more time on hobbies, travel, and visiting family, it also presents unique challenges. Ooma presents a safety guide for seniors, highlighting 30 tips to help them age safely, stay connected, and maintain independence. Instead of a simple list of helpful gadgets, the team created a roadmap to help seniors navigate a rapidly changing world with confidence.
Click below to zoom.
One of the most crucial sections focuses on digital safety and online scam protection. Seniors can use the Internet to learn new things and connect with others, but it’s also full of risks and schemes where criminals prey on uninformed elders. The article explains how to avoid scams with password managers and multi-factor authentication. These tips on strong password creation and extra protection can drastically lower the risk of identity theft and financial loss due to scams.
The following section focuses on physical safety and emergency response. While most of us know to call “911” in an emergency, many of us are unaware of Enhanced 911 (E911), which automatically sends a senior’s address to responders. This is critical if the senior who placed the emergency call cannot speak. A medical ID displayed on a smartphone lock screen can help EMS workers begin treatment instantly and save more lives. Fall detection devices make good use of these services by automatically sharing location and calling for help. These affordable, simple tools can save a senior’s life.
Next, the chart moves on to home security. Smart security cameras and motion-activated systems don’t have to be complicated. They can help seniors reduce stress and increase their peace of mind. Smart doorbells and two-way audio allow them to communicate with visitors without having to go to the door. Environmental monitoring devices are essential for detecting poor air quality and dangerous temperature conditions. Practical advice and the article’s compassionate tone remind readers that safety offers seniors independence.
In that same spirit of independence, the article turns to accessibility. These include visual/hearing alerts, simpler phone interfaces, and medication reminder apps. These tools address health issues that affect all seniors, like hearing loss, vision changes, and memory challenges. These apps and aids will help seniors develop healthy daily routines, reduce frustration, navigate the world, and make the most of their lives.
Lastly, the guide addresses phone safety and scam calls. Seniors can use caller ID authentication and call blocking to reduce fraudulent calls. Unfortunately, seniors are often victims of these scams. While education is also essential for helping seniors navigate these calls, modern VoIP technology and other features make the process much easier. A caller’s sense of urgency can sway them, so these tools can help them avoid the calls altogether.
The team’s tips empower seniors and their loved ones, helping them prepare for the future. This list is a conversation starter to help families plan for independent seniors to live safely and healthily.
-

 Business Visualizations1 year ago
Business Visualizations1 year agoEverything Owned by Apple
-

 Business Visualizations1 year ago
Business Visualizations1 year agoAmerica’s Most Valuable Companies Ranked by Profit per Employee
-
 Business Visualizations1 year ago
Business Visualizations1 year agoThe Biggest Fortune 500 Company in Every State
-

 Business Visualizations10 months ago
Business Visualizations10 months agoThe Biggest Employers by Industry
-
 Business Visualizations2 years ago
Business Visualizations2 years agoNew Animated Map Shows Airbnb’s Fully Booked Cities Along the 2024 Eclipse Path of Totality
-

 Business Visualizations2 years ago
Business Visualizations2 years agoEverything the Luxury Giant LVMH Owns in One Chart
-
 Timelines1 year ago
Timelines1 year agoTimeline Charts the Development of Communications Technology
-

 Charts2 years ago
Charts2 years agoHow Many Crayola Crayon Colors Are There? A Lot.